Wrist tendonitis is a condition that occurs when a tendon swells or becomes inflamed after an impact or injury. This injury can cause stiffness in the wrist and joint pain, as well as affect how the tendon in the wrist moves.
As such, wrist tendonitis could hinder your ability to do day-to-day movements like clenching your fist fully, lifting objects, or typing. Find out how to help treat tendonitis in the wrist using Elastoplast Supports.
What are the symptoms of wrist tendonitis?

There are several symptoms of wrist tendonitis, although the main symptom is pain in the wrist joint. Moreover, this pain can vary and may be dull at first or get gradually worse if the wrist is moved around.
Some other common symptoms of wrist tendonitis include:
- weakness in the wrist
- swelling and inflammation which can make tasks/activities like texting, typing and writing more difficult and can aggravate the injury
- a grating or grinding sensation when moving the wrist, which may also sound like it’s creaking with each movement
- warmth and redness of the wrist
- inability to clench the fist
What are the causes of wrist tendonitis?

Wrist tendon pain is typically caused by repeated stress or trauma, and overuse of the tendons in your wrist. Tendonitis in the wrist can be caused by daily habits or activities like:
- writing with pen and paper for long periods of time
- playing sports that require frequent use of the wrists, like tennis, table tennis or darts
- texting and typing on a computer, as well as using a computer mouse
- playing video games with a controller for extended periods
- carrying out repetitive physical tasks like chopping wood or sweeping the floor
The condition can also be caused by factors which may be predisposed, such as:
- autoimmune disorders or certain health conditions like diabetes, gout, osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis
- having a history of tendon injuries, i.e. from constant overuse due to sporting activities like tennis or gaming
- an injury caused by impact such as a fall
- age, e.g. over the age of 40
- smoking
- poorly aligned joints
- being assigned female at birth
How is wrist tendonitis diagnosed?
Wrist tendonitis is usually diagnosed by a doctor or medical professional who will perform a physical exam by reviewing your symptoms. This could include the doctor asking you to try to move your wrist in certain directions, such as:
- Clenching your fist
- Rotating your wrist
- Bending your wrist frontwards and backwards
- Wrist fractures (breaks in the bones of your wrist)
- Trigger finger which occurs when inflamed tendons cause your finger to be stuck in a bent or disfigured position
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Arthritis which can also cause painful swelling and inflammation in the joints, like wrist tendonitis
Wrist tendonitis vs carpal tunnel syndrome
Some people may confuse wrist tendonitis with carpal tunnel syndrome, and vice versa, due to some similar characteristics in the wrist injury such as the fact they both cause pain and discomfort in the hand and wrist.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when pressure is applied onto a nerve in your wrist. The compressed nerve can cause symptoms such as tingling or numbness in your fingers, thumbs, hands and wrist.
Does wrist tendonitis ever go away?
Tendonitis in the wrist is a condition that can be managed and treated with various methods and treatments. Wrist tendon pain usually subsides and improves with proper injury management by ensuring the wrist is rested. i.e. taking frequent breaks from typing or using your wrists for long periods, medication to manage the pain, and using wrist supports or braces.
Over time, the tendon will heal naturally, provided the correct measures and steps have been taken to ensure the tendons in the wrist are fully healed and rested.
Wrist tendonitis treatment
There are many options to treat wrist tendonitis symptoms and some of these include:
- Medication such as painkillers
- RICE method (rest, ice, compression and elevation)
- Physical or occupational therapy which can help strengthen the wrist and improve range of motion
- Wrist supports
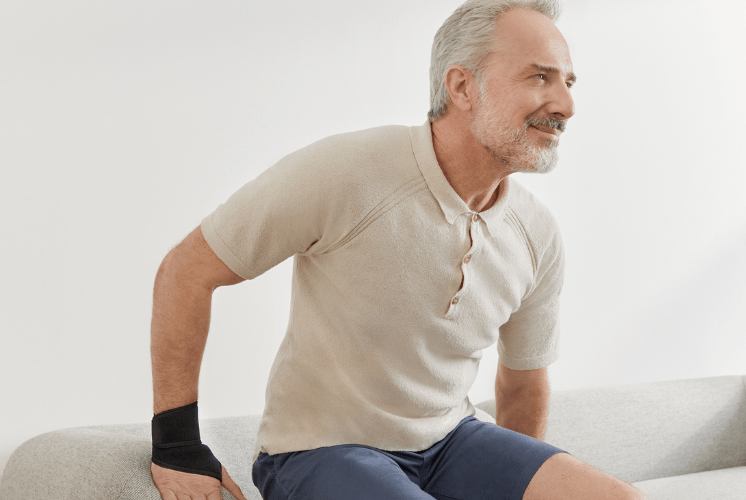
The Elastoplast Protective Wrist Support is designed to provide support, relief and compression to the joint to aid tendonitis in the wrist. With 360 Support Technology, it also provides wraparound support and stability to the wrist, as well as Dynamic Pressure Adjustment that reduces overstraining to relieve pain. This has been tested and recommended by physiotherapists and sports doctors.
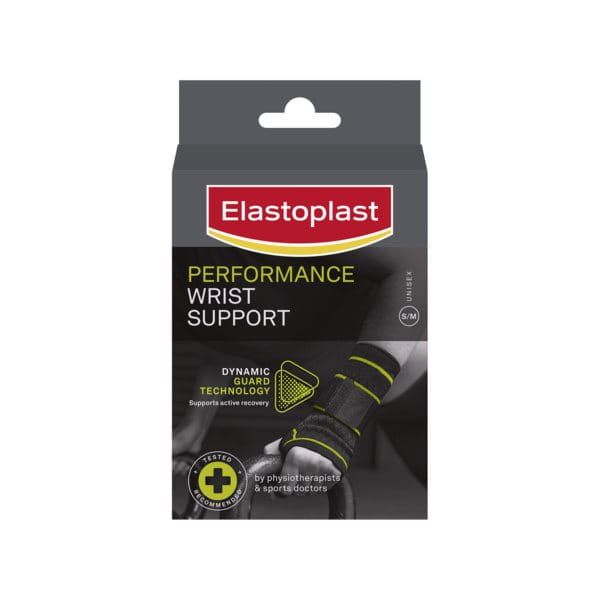
For active athletes that require a moderate level of support to continue playing their sport, the Performance Wrist Support helps provide strength, protection and compression for stiff, weak or painful wrists. This wrist support is designed with Dynamic Guard Technology which supports active recovery.
If pain persists and becomes severe for a long period of time, you are advised to see a doctor or medical professional. They can assess the injury to determine any underlying conditions that may or may not be causing the pain, such as damaged tissue or a ruptured tendon in the wrist.
Should I sleep with a wrist brace on for tendonitis?
Wearing a wrist support or brace during the day is recommended, however, you can also wear the wrist support during the night as you sleep. The maximum hours recommended for wearing a wrist support overnight is 8 hours.
Throughout the day you can remove it now and again to ensure that you exercise the wrist gently to enhance effective recovery. This can be light movements like slowly rotating the wrist or clenching the fist.
Preventing tendonitis in the wrist
Prevention of conditions like tendonitis in the wrist can be difficult, as this can depend on several factors which you may not be able to control, such as things like age or autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis.
However, you can take measures to reduce the risk by:
- not overworking the tendons in your wrist or hand, this can cause swelling and inflammation
- always stretch your wrists before physical activity, especially before sports like tennis
- use a protective wrist brace or support
- take frequent breaks if you do a lot of typing on computers, phones, tablets or other activities that may strain your wrists or fingers.






.jpg?rx=436&ry=0&rw=3223&rh=2160&hash=FA8B83CD5866417422BBD832C005C2E8)