Published: February 2022
Last Reviewed: August 2025
Discover the different types of lacerations, how to treat them with Elastoplast products, and the signs of an infected wound that may need medical care.
Published: February 2022
Last Reviewed: August 2025

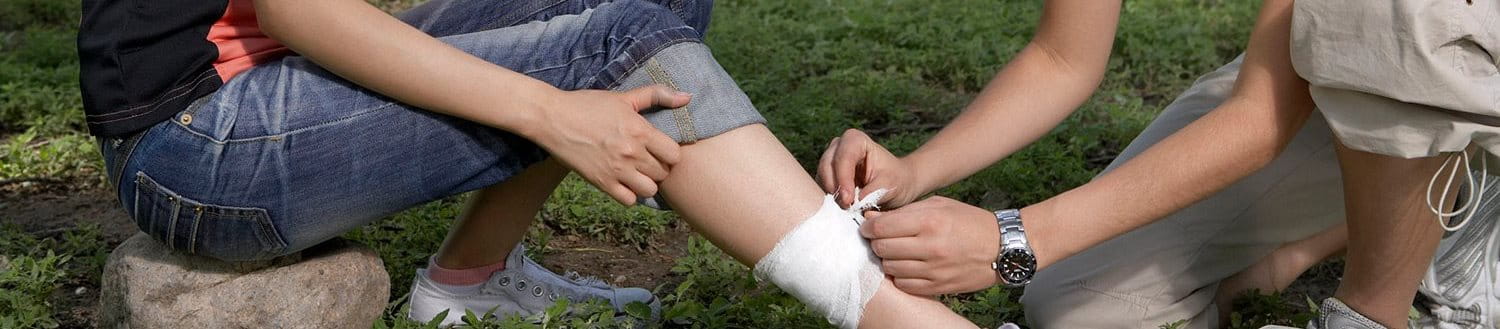
A laceration is a deep cut or tear in the skin and underlying tissue that results in an irregular or jagged wound and may cause heavy bleeding. It is a type of wound that can separate the top layer of skin from the deeper layers and often occurs in areas close to bone, such as the forehead, scalp, shins, elbows, or kneecaps.
The severity can range from mild (affecting only the skin) to severe (involving muscles, blood vessels, or nerves).
Lacerations vs abrasions

Both abrasions and lacerations are open wounds, but they differ in how they occur and appear:
If you think you have an abrasion rather than a laceration, learn more about how to treat abrasions here.
A laceration wound is caused when the skin and underlying tissues are torn or cut, usually by some form of trauma. Common causes include:
Lacerations can happen even during everyday activities, so it’s important to take safety precautions during daily activities when handling sharp or heavy objects.
Linear lacerations
These are the simplest type of laceration. They are usually caused by sharp objects, such as knives, glass, or even paper, and typically affect only the top layer of the skin (the epidermis). The wound edges are straight and clean, making them easier to manage.
Most minor linear lacerations can be treated at home with proper cleaning, disinfection, and a sterile plaster or dressing. However, if the cut is deep, continues bleeding after pressure, or is longer than 2 cm, medical attention is recommended.
Stellate lacerations
Stellate lacerations have a star-shaped appearance and are caused by blunt force trauma, such as being hit with an object or receiving a punch. Because the wound edges are irregular and may involve deeper tissue damage, these lacerations are more complex.
These types of lacerations often require professional medical care, as they may need stitches to heal properly and to reduce the risk of infection or scarring.
Split lacerations
Split lacerations occur when the skin is crushed against an underlying bone and then forced open—for example, when a finger gets caught in a closing door. These wounds often look ragged and can be painful because they involve both the skin and tissues beneath.
Seek medical attention for split lacerations, especially if the wound is deep, bleeding heavily, or located near a joint or tendon, as there is a higher risk of complications.
Degloving laceration
This is a very severe type of wound where the skin is torn away from the underlying tissue, often due to industrial, road, or heavy machinery accidents. A degloving laceration can cause significant blood loss and tissue damage.
Immediate hospital care is essential, as surgery is often required to repair the wound and prevent life-threatening complications.
Lacerations are often severe and usually require medical attention because wide, uneven breaks in the skin can cause heavy bleeding and may need stitches.
Clean your laceration

Firstly, stop the bleeding by applying direct pressure and elevating the wound if possible. Next, it’s important to clean the wound properly to remove dirt and bacteria, which helps prevent infection and promotes optimal healing.
Elastoplast Wound Spray provides an effective and convenient way to clean wounds. This fast, pain-free spray gently washes away dirt, bacteria, and particles without rubbing, which can further irritate the wound. It is also colourless and odourless, making it suitable for children and sensitive skin.
Spray the entire wound area from a distance of about 10 cm, then gently pat it dry with a clean towel or cloth.
Protect your laceration
The second step is to protect the injured skin from dirt and bacteria to prevent infection, ensuring the wound heals undisturbed. Gently dry the surrounding skin and cover the wound with a sterile plaster, wound dressing, or compress from Elastoplast.
The Second Skin Advanced Hydrocolloid Protection XL is a plaster that offers ultra-thin, waterproof protection, accelerating wound healing. The patches are discreet, flexible and create a protective barrier that seals against dirt and bacteria.
Heal your laceration
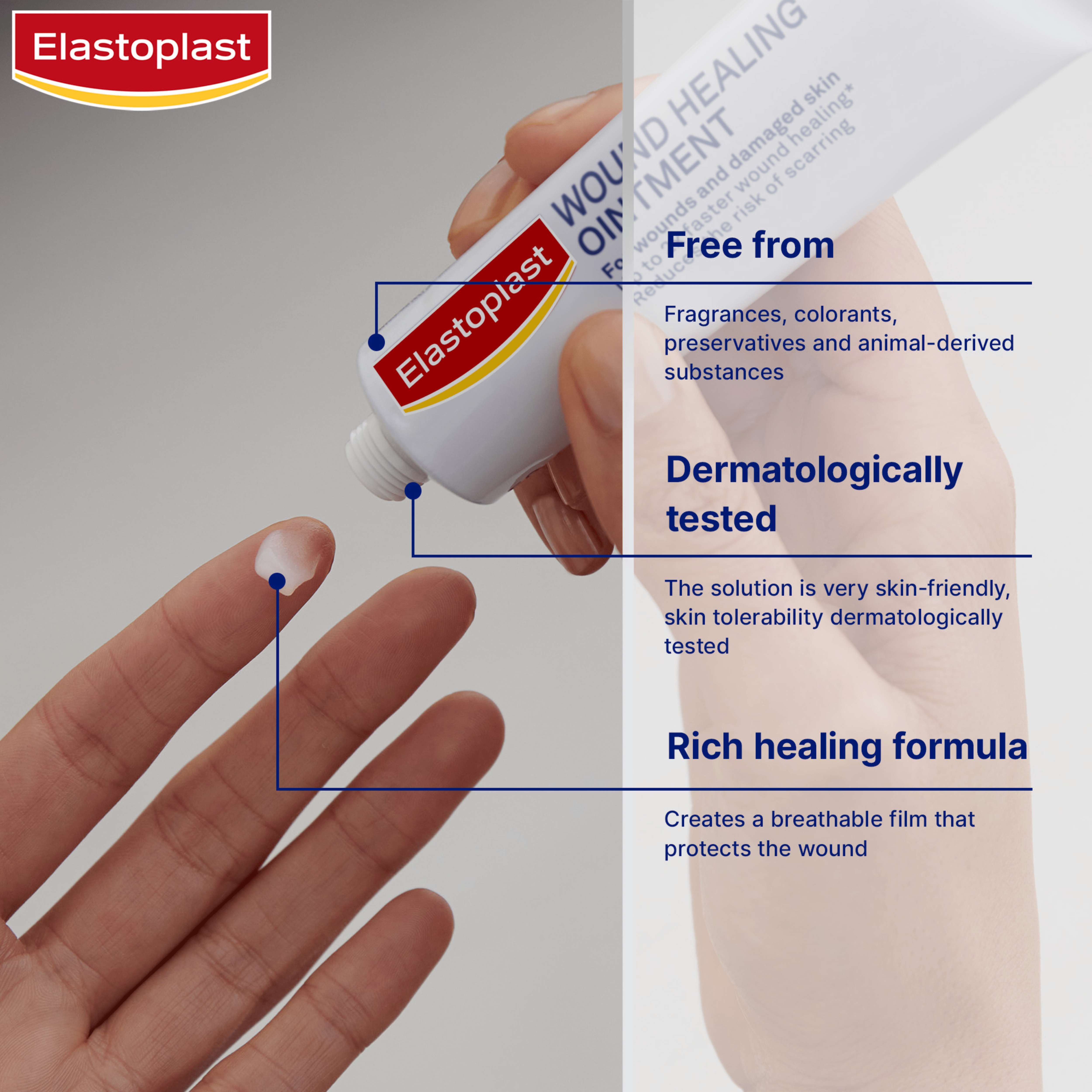
Apply Elastoplast Wound Healing Ointment to help your wound heal safely and fast while also lowering the risk of scarring. The ointment is designed to protect the wound, keep it moist, and support natural healing. Change the dressing daily and reapply the ointment as needed until the wound heals.
When do lacerations need stitches?
For some injuries, especially wide or deep lacerations, stitches or other professional wound closure may be required, such as application of skin glue.
It is advisable to visit a healthcare professional if the wound bleeds for longer than seems reasonable, has particularly jagged edges, or if the skin laceration is located over a joint or somewhere such as the lips or an eyelid. A healthcare professional should remove the stitches, which can usually be done after several days.
When do lacerations need stitches?
You should consult a medical professional for a laceration wound if any of the following apply:
Getting prompt medical attention in these cases helps prevent infection and ensures proper healing.
What is the difference between a cut and a laceration?
A cut generally refers to a wound made by a sharp object, such as a knife, glass, or paper. Cuts tend to have smooth, straight edges, which makes them easier to clean and treat. A laceration is typically a deeper wound caused by blunt trauma or accidents, such as falling, getting hit, or being caught in machinery.
In summary, a cut is usually neat and caused by something sharp, while lacerations can be more irregular and often result from trauma to the skin.
Is a laceration a deep cut?
What is an example of a laceration?
Always see a doctor if the wound is deep, bleeds heavily or shows signs of infection like reddening, swelling or warmth. Please note that, although they were compiled with great care, the tips and advice given on this website by no means substitute medical advice and treatment. If you have or suspect a health problem, consult a doctor and follow medical advice, regardless of what you have learned on this website. Always read carefully and follow the instructions for use or the leaflets of our products.
For further information, please contact us via email at ConsumerRelationsUK@Beiersdorf.com