Wrist arthritis – or arthritis in the wrist – is a condition that often presents itself with wrist pain, stiffness and swelling. There are many different types of wrist arthritis, and the causes can vary. This article will explain this in further detail, alongside the symptoms, diagnosis of the condition and recommended treatment.
Arthritis in wrist symptoms
Wrist arthritis symptoms usually start with general pain and stiffness, although there are some other signs and symptoms, such as:
- Swelling and inflammation
- Clicking, grinding or cracking sounds when moving the wrist
- Weakness in the wrist
- Reduced range of motion
How to tell if you have arthritis in your wrist
Symptoms of wrist arthritis will vary from person to person, which usually depends on the type of arthritis and how severe your condition is. There are usually tell-tale signs that will indicate whether you have wrist arthritis by the severity level.
- Mild: These symptoms can manifest mildly, such as having an unusual feeling within the wrist and experiencing slight wrist joint pain. Things like turning a door handle, gripping a tennis racket or trying to open a jar may be painful. These symptoms can come and go over a period of days or weeks.
- Moderate: Throbbing may feel frequent and is a common symptom for those with moderate arthritis in the wrist, as well as restricted movement. These symptoms may flare-up periodically and may feel worse each time.
- Severe: Severe arthritis in the wrist is apparent when almost any activity involving the wrist joint is extremely difficult and painful. Flare-ups still happen periodically, although the pain is typically constant, even at rest. Motion of the wrist will be extremely difficult, and a physical deformity could be more noticeable over time.
Diagnosing arthritis in wrist
A doctor will be able to diagnose and test for wrist arthritis either by performing a physical examination or by conducting tests such as:
- X-rays to examine the cartilage
- Blood tests
Physical examinations will involve your doctor examining the wrists for swelling, pain and tenderness, as well as checking the location of the swelling to determine which of the wrist joints are impacted the most.
Arthritis in wrist causes

The wrist joint is made up of several bones which are joined together to form the wrist. These bones allow in the wrist to be able to turn and twist in different directions.
Within the wrist joint, cartilage (a connective tissue) is also present at the end of the bones, allowing them to move together. However, cartilage can wear away due to factors such as age and health conditions.
Types of wrist arthritis
Several types of arthritis can affect the wrist, with some being related specifically to autoimmune diseases and arthritis from trauma such as a broken bone or a sprain. These include:
- Psoriatic arthritis: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that causes scaly skin patches. Those with psoriasis can also get psoriatic arthritis in the wrist and other joints in the body.
- Osteoarthritis: This condition is the wearing down of cartilage, and often develops as you age. It occurs naturally due to years of wear and tear on the wrist joint. Osteoarthritis can also be present in the wrist and thumbs.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Similarly to psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease and often appears in small joints like the wrists at the start and can affect both wrists. The immune system attacks and damages healthy cells, including cartilage.
- Post-traumatic arthritis: Arthritis in the wrist can occur after injuries, which can develop quickly after an injury or gradually over time. Injuries like broken bones and sprains can lead to uneven joint surfaces that cause them to wear out.
Other causes of wrist pain
Typing on a computer or laptop for long periods can aggravate wrist joint pain, especially if you already have any of the above conditions. To prevent this, consider using the following:
- Ergonomically designed mouse pads, mouses and keyboards
- Smaller and lighter keyboards
- Voice input and word prediction to reduce typing significantly
How do I know if it's carpal tunnel or arthritis?
Although sharing similar traits, there are some clear differences between carpal tunnel syndrome and wrist arthritis. These include:
- The areas of the hand and wrist that are affected
- The type of pain you might feel
- Why you might find daily activities difficult
Arthritis in wrist vs wrist tendonitis
You may also confuse wrist arthritis with wrist tendonitis, due to the shared pain in the wrist for both conditions, however wrist tendonitis specifically relates to issues with the tendons.
How to treat arthritis in wrist
Treating wrist arthritis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. It may be helpful to wear a wrist brace to help support and stabilise the wrist. It’s important to seek medical advice from a doctor for thorough examination and treatment recommendations.
Wrist support for arthritis
The Elastoplast Protective Wrist Support is designed with a Dynamic Pain Guard which provides protection and relief in the wrist, as well as supporting weak wrists that may have been injured or are recovering from treatment.
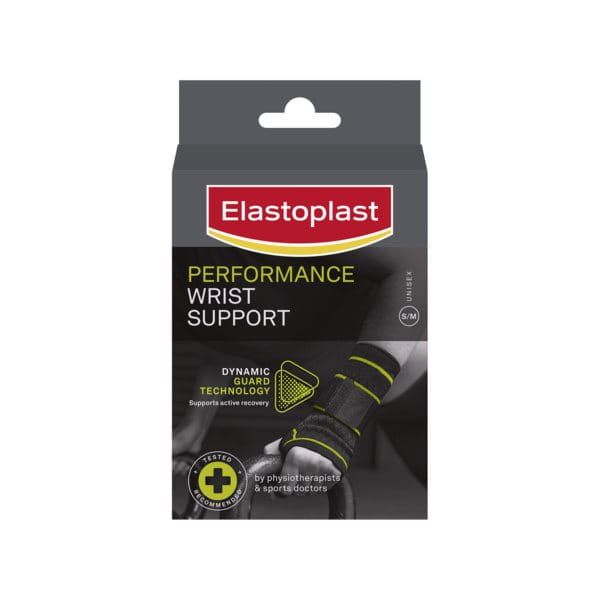
For those participating in sports and other types of physical activity experiencing wrist arthritis, the Elastoplast Performance Wrist Support provides a moderate level of support to the wrist during sports activities. This helps to provide strength, protection, compression and comfort to stiff, weak or painful wrists.
Other treatments for wrist arthritis
Wrist arthritis is manageable with various treatments, which can be:
- Over-the-counter medicines like ibuprofen for pain relief
- Steroid injections (also known as a cortisone injection) for temporary pain relief and inflammation reduction
- Hot and cold therapy
- Exercises involving the wrist to alleviate wrist joint pain
These treatments are only recommended as temporary pain relief when flare-ups of wrist arthritis occur.
Surgery could also be required, and this will depend on the severity of the injury. These include:
- Denervation: A simpler surgery which involves the surgeon removing nerves that go into the wrist joint. These nerves are not connected to the skin so there is no numbness after the surgery. Recovery is relatively straightforward; however, this type of surgery is often not a permanent solution to wrist arthritis.
- Fusion surgery: This involves joining one or more of the wrist bones to prevent rubbing and friction.
- Proximal row carpectomy: Removal of a few carpal bones in the wrist to allow the bones more room to move without rubbing or causing friction.
- Joint replacement (wrist arthroplasty): This procedure involves the removal of damaged cartilage and bone in your wrist, which is replaced with artificial material such as metal or plastic to restore the function of the wrist joint.
How to prevent arthritis in wrist
Unfortunately, wrist arthritis is not a condition that can often be prevented. However, once arthritis in the wrist develops, you can take some steps to help alleviate any discomfort and pain. These include wearing wrist supports to take pressure off the wrist, avoiding repetitive motions, and performing exercises for the hands and wrists such as hand stretches or grip exercises.